Test deconvolution imports#
Before testing the dependencies make sure you are in the new devbio-napari based environment you created in the last section. Type the following.
mamba activate decon-dl-env
Now test whether the dependencies have been installed properly
try:
import imnotthere as int
imnothtere_found=True
print('ImNotThere found')
except ImportError:
imnotthere_found=False
print('!ImNotThere NOT found')
try:
from clij2fft.richardson_lucy import richardson_lucy_nc
clij2_rl_found=True
print('clij2fft found')
except ImportError:
clij2_rl_found=False
print('!clij2fft NOT found')
try:
import RedLionfishDeconv as rl
redlionfish_rl_found=True
print('RLF found')
except ImportError:
redlionfish_rl_found=False
print('!RLF NOT found')
try:
import cupy as cp
from tnia.deconvolution.richardson_lucy import richardson_lucy_cp
cupy_found=True
print('cupy found')
except ImportError:
cupy_found=False
print('!cupy NOT found')
import numpy as np
!ImNotThere NOT found
clij2fft found
RLF found
cupy found
Get test data#
Get images and models from this link https://www.dropbox.com/scl/fo/yc5jaoj3ap936dqqy8urc/h?rlkey=ho8vp2nbvprzyltytryj9demp&dl=0
Place both the
dataandmodelsfolders beside thedocsfolder.Use imread to verify you can open the image, then print the size of the image and verify it is
(128,256,256)
from skimage.io import imread
from pathlib import Path
# local path to the data folder
image_path = Path('../../data/deconvolution/')
image_name='Bars-G10-P30-stack.tif'
psf_name='PSF-Bars-stack.tif'
truth_name='Bars-stack.tif'
im=imread(image_path / image_name)
psf=imread(image_path / psf_name)
truth=imread(image_path / truth_name)
im=im.astype('float32')
psf=psf.astype('float32')
psf=psf/psf.sum()
print(im.shape, psf.shape, truth.shape)
(128, 256, 256) (128, 256, 256) (128, 256, 256)
View 3D Data in notebook#
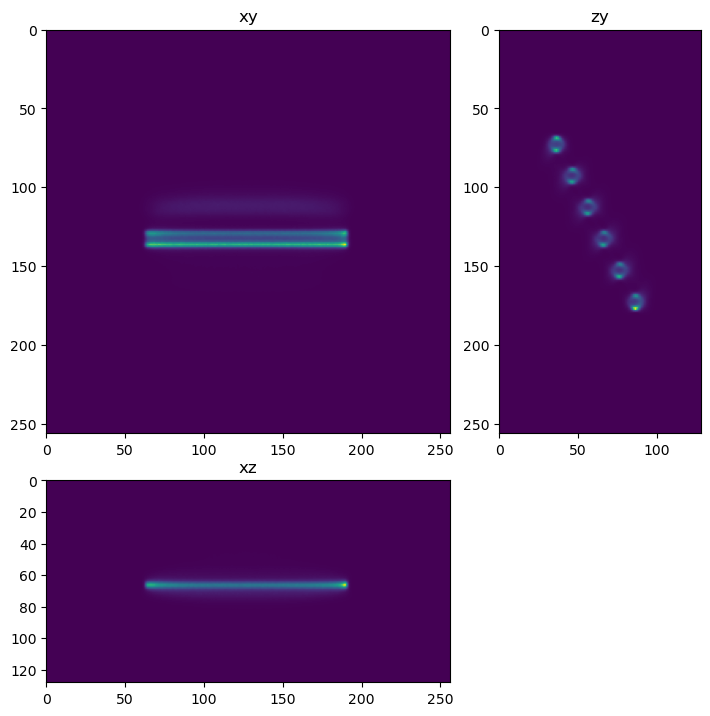
View the data using the xy, xz, and zy max projections from tnia-python.
from tnia.plotting.projections import show_xyz_slice_center
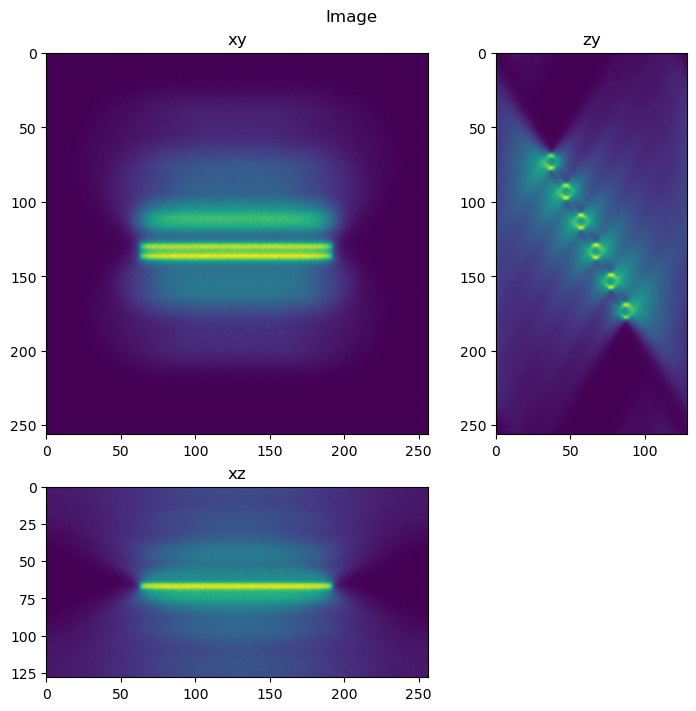
fig = show_xyz_slice_center(im, figsize=(7,7))
fig.suptitle('Image')
Text(0.5, 0.98, 'Image')
Use stackview to explore data#
Alternatively we can use the stackview library to explore the data.
import stackview
stackview.orthogonal(psf, continuous_update=True)
stackview.orthogonal(truth, continuous_update=True)
stackview.orthogonal(im, continuous_update=True)
import helper and show image#
import sys
sys.path.append('../')
import decon_helper as dh
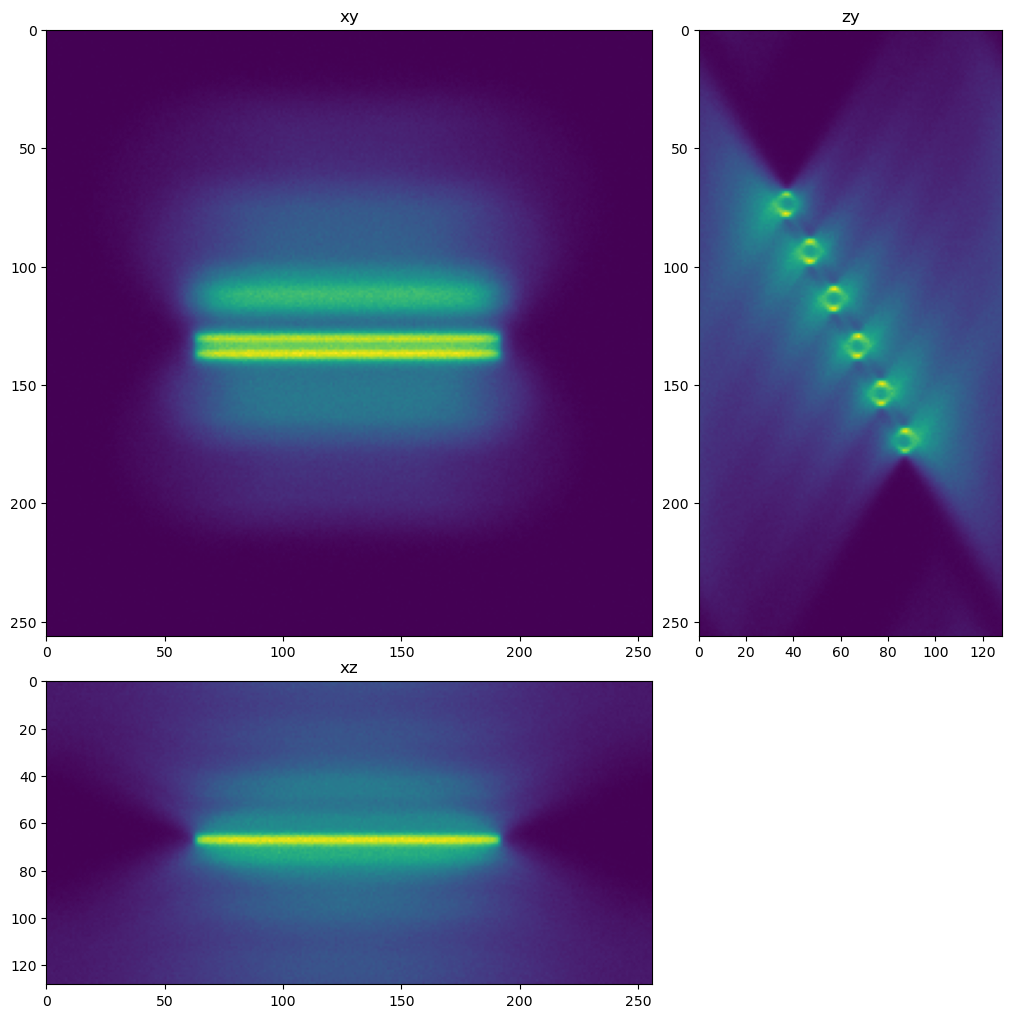
dh.show_xyz_slice(im, 'tnia')
tnia available
stackview available
Import deconvolution libraries#
Try importing the clij2 and redlionfish implementations of Richardson Lucy. If they are found perform a deconvolution with each library
try:
from clij2fft.richardson_lucy import richardson_lucy_nc
clij2_rl_found=True
except ImportError:
clij2_rl_found=False
try:
import RedLionfishDeconv as rl
redlionfish_rl_found=True
except ImportError:
redlionfish_rl_found=False
try:
from tnia.deconvolution.richardson_lucy import richardson_lucy_cp
tnia_rl_cupy_found=True
except ImportError:
tnia_rl_cupy_found=False
print('clij2 rl found',clij2_rl_found)
print('redlionfish rl found',redlionfish_rl_found)
print('tnia rl cupy found',tnia_rl_cupy_found)
clij2 rl found True
redlionfish rl found True
tnia rl cupy found True
Deconvolve with clij2#
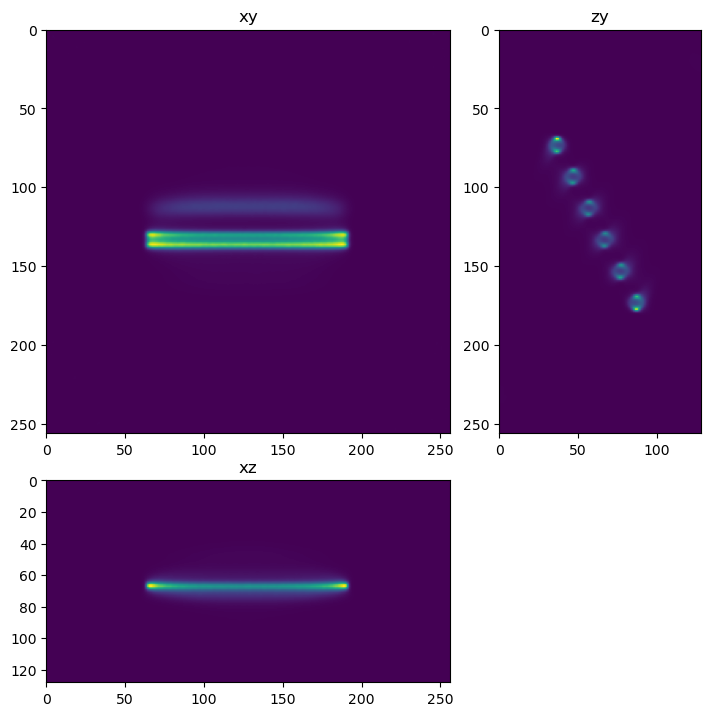
if clij2_rl_found==True:
decon_clij2=richardson_lucy_nc(im,psf,100,0)
show_xyz_slice_center(decon_clij2,figsize=(7,7))
else:
print('clij2 not found')
decon_clij2=np.zeros_like(im)
get lib
calling convcorr 0 0
Deconvolve with tnia-cupy#
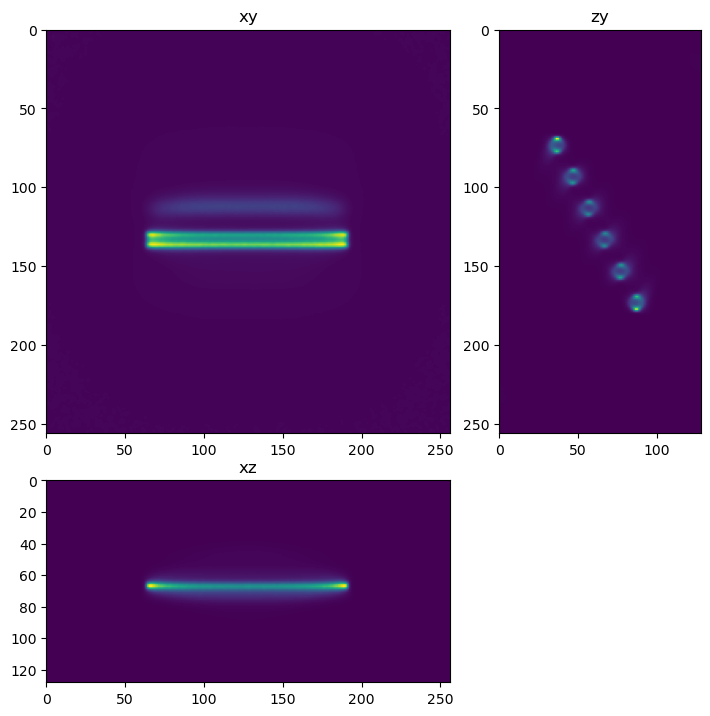
if tnia_rl_cupy_found:
decon_tnia=richardson_lucy_cp(im,psf,100,True)
show_xyz_slice_center(decon_tnia,figsize=(7,7))
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
Look at the deconvolution result with stackview#
stackview.orthogonal(decon_clij2, continuous_update=True)
Deconvolve with redlionfish#
if redlionfish_rl_found==True:
decon_rlf=rl.doRLDeconvolutionFromNpArrays(im, psf, niter=100, method='gpu', resAsUint8=False )
else:
print('redlionfish not found')
decon_rlf=np.zeros_like(im)
fig=show_xyz_slice_center(decon_rlf, figsize=(7,7))
View data in Napari and ask questions#
View the data in Napari, switch to a 3D view and rotate and explore the dataset? How good is the reconstruction? Is it a truer representation of the data as compared to the image?
Excercise: Deconvolve the data for 1000 iterations, or 10,000 if you have a fast GPU (or even 100,000 if you have a fast GPU and a bit of time). Does the reconstruction continue to improve with more iterations?
import napari
viewer=napari.Viewer()
viewer.add_image(im)
viewer.add_image(decon_clij2)
viewer.add_image(decon_rlf)
viewer.add_image(truth)
<Image layer 'truth' at 0x1d228e14bb0>
